Navigating the financial markets can often feel like piecing together a complex puzzle, with traders constantly on the lookout for patterns that inform their decisions. Among these, the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern emerges as a particularly captivating concept. When paired with Fibonacci ratios—especially the .328 and 1.27 levels of the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern—it provides valuable insights into price fluctuations and facilitates more informed trading strategies.
Whether you’re an experienced trader or just beginning your journey, understanding the intricacies of the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern can significantly enhance your approach to trading. In this exploration, we’ll unpack the essentials of the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern and examine how integrating Fibonacci ratios can elevate your trading strategies to new heights.
Understanding the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27Pattern
The abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern represents a three-wave formation commonly observed in both bullish and bearish market conditions. It comprises the following components:
- Wave A: This is the initial movement that goes against the prevailing market trend, signaling a potential reversal.
- Wave B: A corrective wave that retraces a portion of Wave A, providing insight into the market’s reaction.
- Wave C: The concluding wave, which typically extends below the low of Wave A in a bearish context or above the high in a bullish context.
Traders leverage this pattern to forecast potential future price movements, drawing from the historical relationships established between the various waves.
The .328 1.27 Configuration
The term “.328 1.27” denotes specific Fibonacci retracement levels associated with the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern:
- 0.328 (32.8%): This level often acts as a critical retracement point for Wave B. A retracement reaching this level indicates a high probability of trend continuation once Wave B concludes.
- 1.27 (127%): This level is employed to project the likely endpoint of Wave C. If Wave C surpasses the low of Wave A and reaches the 1.27 level, it signifies strong momentum in the price movement, suggesting a possible continuation of the trend or a reversal.
By understanding these configurations, traders can better navigate price movements and make informed decisions in the financial markets.
Understanding The abc .328 1.27.328 1.27Pattern
The abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern represents a three-wave formation commonly observed in both bullish and bearish market conditions. It comprises the following components:
- Wave A: This is the initial movement that goes against the prevailing market trend, signaling a potential reversal.
- Wave B: A corrective wave that retraces a portion of Wave A, providing insight into the market’s reaction.
- Wave C: The concluding wave, which typically extends below the low of Wave A in a bearish context or above the high in a bullish context.
Traders leverage this pattern to forecast potential future price movements, drawing from the historical relationships established between the various waves.
The .328 1.27 Configuration
The term “.328 1.27” denotes specific Fibonacci retracement levels associated with the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern:
- 0.328 (32.8%): This level often acts as a critical retracement point for Wave B. A retracement reaching this level indicates a high probability of trend continuation once Wave B concludes.
- 1.27 (127%): This level is employed to project the likely endpoint of Wave C. If Wave C surpasses the low of Wave A and reaches the 1.27 level, it signifies strong momentum in the price movement, suggesting a possible continuation of the trend or a reversal.
By understanding these configurations, traders can better navigate price movements and make informed decisions in the financial markets.
Understanding The abc .328 1.27.328 1.27Pattern
The abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern represents a three-wave formation commonly observed in both bullish and bearish market conditions. It comprises the following components:
- Wave A: This is the initial movement that goes against the prevailing market trend, signaling a potential reversal.
- Wave B: A corrective wave that retraces a portion of Wave A, providing insight into the market’s reaction.
- Wave C: The concluding wave, which typically extends below the low of Wave A in a bearish context or above the high in a bullish context.
Traders leverage this pattern to forecast potential future price movements, drawing from the historical relationships established between the various waves.
The .328 1.27 Configuration
The term “.328 1.27” denotes specific Fibonacci retracement levels associated with the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern:
- 0.328 (32.8%): This level often acts as a critical retracement point for Wave B. A retracement reaching this level indicates a high probability of trend continuation once Wave B concludes.
- 1.27 (127%): This level is employed to project the likely endpoint of Wave C. If Wave C surpasses the low of Wave A and reaches the 1.27 level, it signifies strong momentum in the price movement, suggesting a possible continuation of the trend or a reversal.
By understanding these configurations, traders can better navigate price movements and make informed decisions in the financial markets.
The Origins Of Fibonacci Ratios
Fibonacci ratios trace their origins back to the 13th century, introduced by the Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, widely known as Fibonacci. He unveiled these ratios in his influential book, “Liber Abaci,” which also presented the famous numerical sequence that carries his name.
The Fibonacci sequence begins with the numbers 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is derived from the sum of the two preceding ones. This sequence manifests in various aspects of nature—observations can be made in the arrangement of flower petals, the spirals of pine cones, and the patterns found in seashells, all showcasing the inherent beauty of this mathematical principle.
As time progressed, traders recognized the relevance of these ratios in the financial realm. They pinpointed critical levels for price retracement and extension based on Fibonacci calculations. The most frequently utilized ratios from this sequence include 0.618 (known as the golden ratio), 0.382, and 0.236.
With increasing awareness among traders, Fibonacci tools became integral to technical analysis. Their significance transcends mere mathematics, echoing the patterns found in nature.
How To Compute Fibonacci Levels
Calculating Fibonacci levels is a straightforward process once you understand the underlying concept. Begin by identifying a notable price swing, which could be defined by a peak and a trough on the price chart of any asset.
Measure the distance between these two points, establishing a baseline for your calculations.
Next, apply the key Fibonacci ratios: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and occasionally 78.6%. Multiply the measured distance by each of these ratios to identify potential support and resistance levels.
Depending on whether you are analyzing an upward or downward movement, add or subtract these values from your starting point.
Be sure to mark these levels on your chart, as they can offer valuable insights into where price reversals or continued trends might occur.
Additionally, consider experimenting with different time frames, as strategies that work for day trading may vary significantly from those suited for longer-term trading approaches.
The Origins Of Fibonacci Ratios
Fibonacci ratios trace their origins back to the 13th century, introduced by the Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, widely known as Fibonacci. He unveiled these ratios in his influential book, “Liber Abaci,” which also presented the famous numerical sequence that carries his name.
The Fibonacci sequence begins with the numbers 0 and 1, and each subsequent number is derived from the sum of the two preceding ones. This sequence manifests in various aspects of nature—observations can be made in the arrangement of flower petals, the spirals of pine cones, and the patterns found in seashells, all showcasing the inherent beauty of this mathematical principle.
As time progressed, traders recognized the relevance of these ratios in the financial realm. They pinpointed critical levels for price retracement and extension based on Fibonacci calculations. The most frequently utilized ratios from this sequence include 0.618 (known as the golden ratio), 0.382, and 0.236.
With increasing awareness among traders, Fibonacci tools became integral to technical analysis. Their significance transcends mere mathematics, echoing the patterns found in nature.
How To Compute Fibonacci Levels
Calculating Fibonacci levels is a straightforward process once you understand the underlying concept. Begin by identifying a notable price swing, which could be defined by a peak and a trough on the price chart of any asset.
Measure the distance between these two points, establishing a baseline for your calculations.
Next, apply the key Fibonacci ratios: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and occasionally 78.6%. Multiply the measured distance by each of these ratios to identify potential support and resistance levels.
Depending on whether you are analyzing an upward or downward movement, add or subtract these values from your starting point.
Be sure to mark these levels on your chart, as they can offer valuable insights into where price reversals or continued trends might occur.
Additionally, consider experimenting with different time frames, as strategies that work for day trading may vary significantly from those suited for longer-term trading approaches.
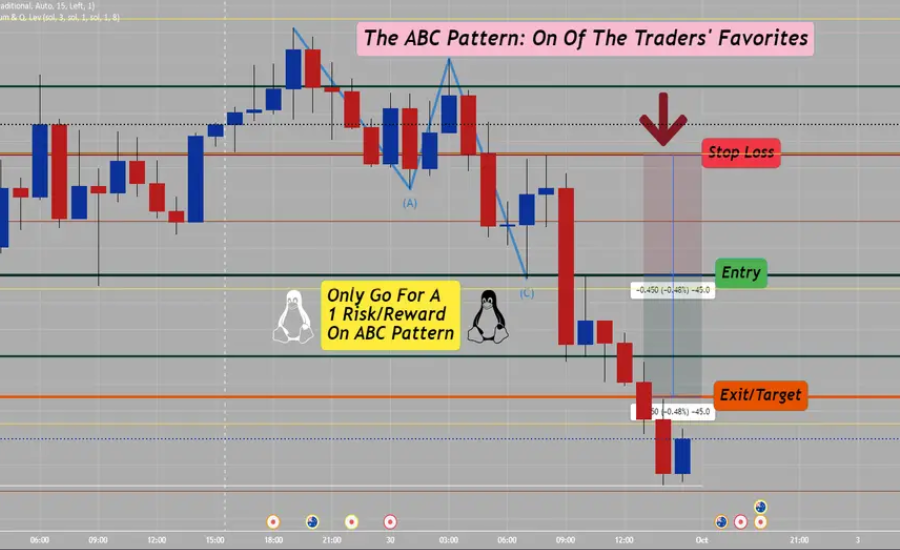
Identifying The abc .328 1.27.328 1.27Pattern .328 1.27 on Trading Charts
Recognizing the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern .328 1.27 on trading charts requires a thoughtful approach and a solid grasp of price movements. Follow these steps to locate the pattern effectively:
Step 1: Identify the Initial Move
Start by pinpointing the movement from point A to point B, which signifies a notable price change, either upward or downward. This initial movement is crucial as it establishes the foundation of the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern.
Step 2: Assess the Retracement
Next, focus on the retracement from point B to point C. Utilize the Fibonacci retracement tool to evaluate this movement. A retracement that hits approximately the 38.2% level serves as confirmation of the .328 retracement within the pattern.
Step 3: Project the Extension
Finally, employ the Fibonacci extension tool to project the movement from point C to point D. The target is the 1.27 extension level, which signifies the completion of the pattern and indicates a potential reversal or continuation of the existing trend.
Practical Tips For Identifying the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27Pattern
- Incorporate Candlestick Patterns: Enhance the precision of your identification by analyzing candlestick patterns alongside the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern.
- Use Volume Analysis: Validate the pattern with volume data, as strong volume can provide additional support for trend continuation.
- Apply Across Different Timeframes: Test this pattern across various timeframes to confirm its validity in different trading scenarios.
By following these steps and tips, you can increase your chances of accurately identifying the abc .328 1.27.328 1.27pattern .328 1.27, allowing for more informed trading decisions.
Tips For Effectively Utilizing Fibonacci Ratios in Trading
Grasping the concept of Fibonacci ratios is just the first step; effectively incorporating them into your trading strategy is essential for success. Here are some practical tips to help you leverage Fibonacci ratios more efficiently:
- Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels: Start by pinpointing significant support and resistance levels on your charts. Fibonacci retracement levels are often found at these points, where price reversals are likely to occur.
- Monitor Market Trends: Pay attention to the overall market trends. When a trend coincides with a Fibonacci level, it may indicate a stronger likelihood of a reversal or continuation, enhancing your trading decisions.
- Combine with Additional Indicators: Enhance your analysis by using other indicators, such as moving averages or volume analysis, alongside Fibonacci ratios. This multi-dimensional approach provides additional validation for your entry and exit points.
- Practice Patience: In trading, timing is crucial. Exercise patience and wait for clear signals that align with Fibonacci levels before entering a trade. Avoid rushing into decisions without sufficient confirmation.
- Analyze Historical Performance: Keep a record of your past trades involving Fibonacci ratios. Reviewing historical performance can offer valuable insights, helping you refine your strategy and improve your future trading decisions.
By implementing these tips, you can better harness the power of Fibonacci ratios, leading to more informed and effective trading strategies.
FAQs About Fibonacci Ratios in Trading
1. What are Fibonacci ratios?
Fibonacci ratios are numerical values derived from the Fibonacci sequence, which are often used in technical analysis to identify potential support and resistance levels in financial markets. Common ratios include 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%.
2. How do I calculate Fibonacci levels?
To calculate Fibonacci levels, identify a significant price swing (a peak and trough), measure the distance between them, and apply the key Fibonacci ratios to find potential support and resistance levels.
3. Can Fibonacci ratios predict market trends?
While Fibonacci ratios can indicate potential reversal points and help traders make informed decisions, they should not be relied upon solely to predict market trends. It’s important to use them in conjunction with other technical indicators.
4. How do I use Fibonacci ratios with other indicators?
Combine Fibonacci ratios with other technical tools, such as moving averages or momentum indicators, to strengthen your analysis. This multi-faceted approach helps confirm entry and exit points.
5. What timeframes are best for using Fibonacci ratios?
Fibonacci ratios can be applied to various timeframes, including intraday, daily, and weekly charts. The effectiveness of the ratios may vary depending on your trading strategy and the timeframe you choose.
Conclusion
Fibonacci ratios are a powerful tool for traders looking to enhance their technical analysis and identify potential price reversals in the market. By understanding how to calculate these levels and effectively incorporating them into your trading strategy—alongside other indicators and sound market analysis—you can make more informed decisions. Remember to practice patience and analyze historical performance to refine your approach over time. With a comprehensive understanding of Fibonacci ratios, you can significantly improve your trading outcomes and navigate the complexities of financial markets with greater confidence.
Stay in touch with us for more updates and alerts! Ventstribune

